If software is eating the world, AI and agentic technology are making a push to revolutionize software development, as recent releases from the likes of Tabnine, Zencoder and Microsoft, among others indicate.
Coding agents are taking on tasks such as intelligent code generation, code repair, test generation, code reviews and real-time optimization.
For instance, Tabnine introduced its Tabnine Code Review Agent in preview as the first AI agent that can incorporate and enforce company-specific development standards, Peter Guagenti, president of Tabnine, told The New Stack.
The product converts plain language requirements into comprehensive review rules, reviews code both at the pull request stage and within the IDE and provides suggested fixes, not just flagging issues.
Guagenti said key differentiators of the Tabnine code review agent include personalization — as it adapts to each team’s methods and preferences, along with ease of use and comprehensive coverage, as it reviews against both company-specific and industry standard rules.
“Right now, these tools are very powerful, and they’re emerging really fast, but they’re behaving sort of like an engineer off the street,” Guagenti said. “Our mission at Tabnine is to have a product that behaves like an onboard engineer who knows your company, knows your team.”
When developers create a pull request, the Tabnine Code Review Agent checks the code in the pull request against the rules established by their team. If any aspect of the code doesn’t conform with those rules, then the agent flags it to the code reviewer, providing guidance on the issue and suggested edits to fix it, the company said.
“AI is already in use in limited ways reviewing and validating code. However, like the static code analysis tools that came before them, current AI tools have been limited to checking code against generic, predefined standards,” wrote Shantanu Kedar, senior director of product marketing at Tabnine, in a blog post. “The challenge is that every mature engineering organization has unique and intricate ways of creating software applications. What one team sees as their irrefutable standard, another team might reject outright.”
Guagenti said the code review agent offers automatic fixes rather than just identifying issues like static analysis tools. It supports over 600 languages and frameworks and uses various large-language models (LLMs) with custom prompt engineering.
The product is now in private preview with Tabnine’s enterprise customers, several with large enterprise engineering teams. Current customers include chip makers, military/government institutions, financial services, and pharmaceutical companies, he said, noting that the company will also offer a simplified version of the technology for individual developers via credit card purchase.
Tabnine uses a “three-legged stool” approach:
And the product includes a proprietary context engine that understands company-specific code patterns and standards
Guagenti said his vision is to provide developers with 10x productivity gains, whereas current tools achieve 20% to 50% gains. “They’re not even doubling yet,” he said.
Overall, the company positions itself as moving beyond generic AI assistance to provide contextually aware, organization-specific code review and development support, he said.
“A lot of time is lost in these engineering reviews. The most senior people are the ones who are doing these reviews,” Guagenti told The New Stack. “And even with those most senior people doing it, not only are they spending a ton of time on it, they’re still missing stuff.”
Meanwhile, Zencoder, a new AI coding assistant company, recently launched its platform and AI agents that compete with GitHub Copilot and other coding tools. The company focuses on production-ready code rather than demos and uses what they call “compound AI systems” that combine traditional development tools (compilers, linters, etc.) with AI capabilities, Andrew Filev, founder and CEO of the startup, told The New Stack.
After a year in development and 500 companies in early access, Zencoder has delivered features including code completion, repository-aware AI chat, and coding agents for tasks like unit testing.
The company predicts significant automation of routine engineering work within four years while emphasizing the continuing importance of human creativity and system thinking.
The Zencoder tools work with Visual Studio Code and JetBrains IDEs and support major languages like Java, C#, and JavaScript.
According to the company, Zencoder’s primary technology pillars include:
“We’re one year old, and we build the product that competes with the best… And it took them three years to build that product,” Filev told The New Stack, aiming his sights at GitHub.
Filev said he believes that in the next four years, we’ll get to the point where AI will be able to automate about half of all the routine work in engineering.
However, “It’s not just like, oh, you give it to LLM, and LLM gives you the perfect answer. That’s not how I see the industry evolving… I see the industry evolving… building what’s called compound AI systems.”
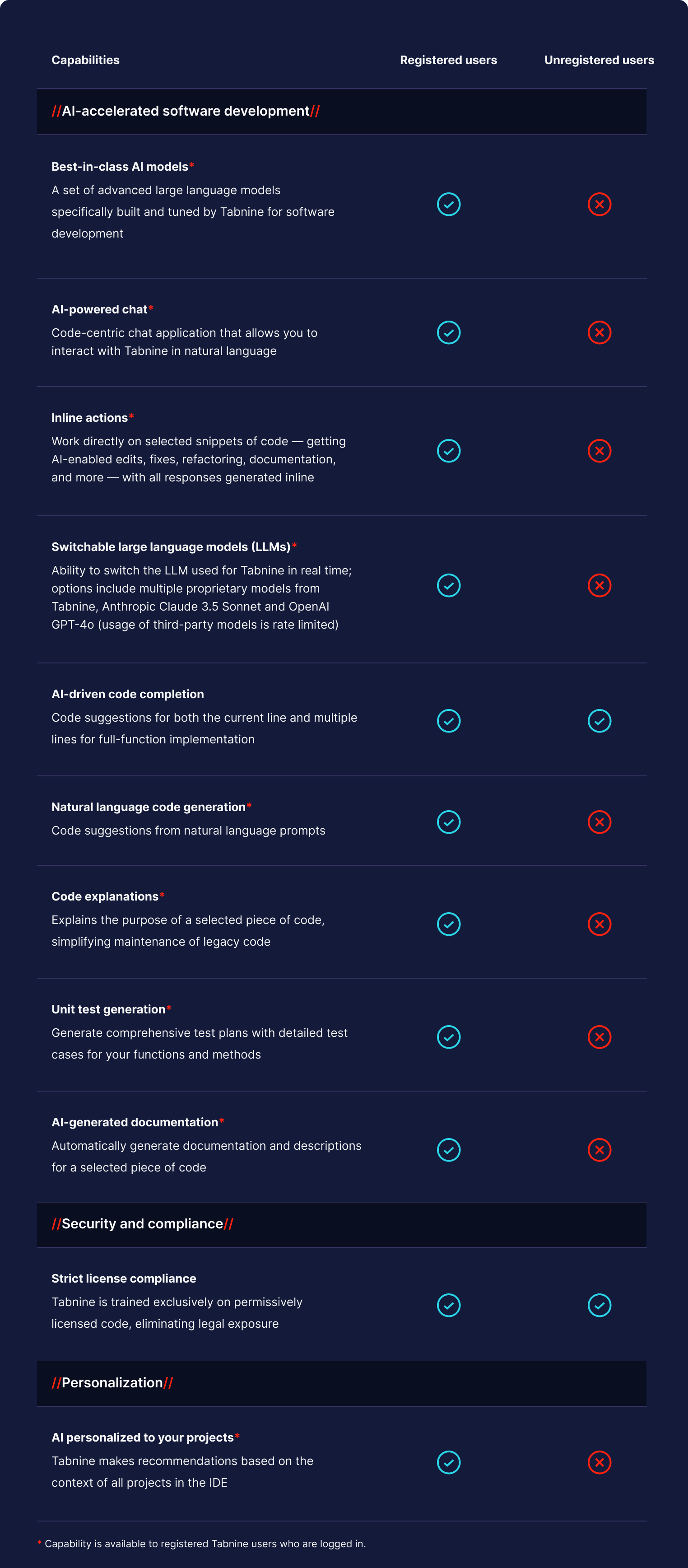
In November, Tabnine released major upgrades to our free AI code assistant, including access to more AI agents, advanced personalization features, and many others. We’ve also added support for Jira Cloud for our Enterprise self-hosted customers, enabling smarter workflows and enhanced productivity. Lastly, we’ve continued to refine our Tabnine AI Chat experience, making interacting with the chat easier and more resourceful.
In a world filled with rising costs, big tech price hikes, and “shrinkflation,” it’s great when you get more value for your money. It’s even better when you get more for free. With this in mind, we’ve made significant additions to our free AI code assistant, Tabnine Basic, including access to more AI agents, advanced personalization features, and the ability to use Claude 3.5 Sonnet as the basis for Tabnine’s code generation and validation features.
If you’re an existing Tabnine Basic plan user, we encourage you to register (if you haven’t already) and update your Tabnine plugin to take advantage of the latest capabilities. To unlock all the capabilities, you need to register for Tabnine and be logged in. Registering for Tabnine involves creating an account and providing us your email address — no credit card is required.
Check out our announcement blog post to learn more about all of the upgrades to our free AI code assistant.
We’re excited to announce that Tabnine Enterprise (self-hosted) now supports seamless integration with Jira Cloud. You can easily connect your Jira Cloud boards to Tabnine, enabling smarter workflows and enhanced productivity. Streamline task management and stay aligned with your team without leaving your editor.
Connecting Tabnine to Jira gives you access to our Jira Implementation Agent and Jira Validation Agent. Tabnine implements Jira issues and generates code from the requirements in the issues, and validates code to verify that it captures the requirements in a Jira issue, providing guidance and code suggestions if it doesn’t.
Read our Jira Integration Docs to learn more.
Within VS Code and JetBrains, Tabnine users can utilize @mentions to search for files according to their project reference beyond just searching for them by name, while staying within Inline Actions. By allowing the prompt to incorporate project references (e.g., functions, constants, objects, etc.), it becomes more intelligent and context-sensitive, leading to better, more precise results that align with the specific project context. It also saves time and enhances productivity, particularly in large codebases.
Open Tabnine Chat now without having to remove yourself from your flow state with the updated keybinding:
In addition to these capabilities, we also made numerous enhancements to Tabnine Enterprise self-hosted. Check out the release notes to learn more.
With the upgraded Basic plan, improvements to our Tabnine Inline Actions experience, and evergrowing list of supported integrations, November’s updates reflect our dedication to making Tabnine the ultimate AI code assistant. We’re thrilled for developers to dive into these new features and boost their workflow efficiency.
Keep an eye out for future announcements!
AWS re:Invent in Las Vegas was a blast. The Tabnine booth had a huge crowd each day, and we gave away three pairs of Meta Ray-Ban Smart Glasses along with free 1-year subscriptions to Tabnine Dev.
In our conversations with customers and attendees, several things stood out that got people excited about Tabnine and conveyed what makes us different from any other AI code assistant vendor in this space today — and why enterprise-grade engineering organizations choose us over vendors like GitHub Copilot and countless others in POC evaluations.

Tabnine’s AI agents and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) models have been evaluated by multiple analyst firms and are proven to generate best-in-class performance for AI code assistants. When compared against all 12 leading vendors in this space, Tabnine was top-ranked by Gartner© in all 5 use cases in the 2024 AI Code Assistant Critical Capabilities Report.
Tabnine’s AI code assistant is the best choice for enterprise companies in highly regulated and privacy-conscious industries. Unlike other vendors in the AI code assistant space, Tabnine can be deployed on-premises on your own servers and via VPC through AWS, GCP, or Azure. You can also run Tabnine in a completely air-gapped environment.
With an on-premises installation, the solution is completely self-contained and lives entirely within your architecture. If you opt for VPC, the entire solution lives on your private cloud. This completely eliminates any risk of exposing your sensitive IP or data to third-party vendors. You can learn more about our private deployments and how we meet all enterprise security and compliance requirements.

We originated the AI code assistant category launching our first AI in 2018. Since then, we’ve led the market in delivering innovative capabilities in this space. We were the first to bring private deployments, local context awareness, model flexibility, codebase connection, Jira integration, AI agents for every step of the SDLC, model fine-tuning, and customized Code Review agents. When you’re thinking about selecting an AI code assistant vendor, think about who you think is going to deliver the most innovation for the enterprise the fastest — and on that metric, Tabnine continues to be the category leader.
We also have a unique perspective on how to maximize the performance of an AI code assistant by leveraging three factors:: LLMs, AI agents, and personalization through RAG.
Tabnine was the first AI code assistant to offer model flexibility. Our agentic and RAG enhancements are fully model-agnostic and significantly improve the relevance of AI-generated code, leading to significant improvements on code acceptance rates.
With our model flexibility, you can connect any LLM or SLM model to Tabnine with an API call. Additionally, if you’re running Tabnine on-premises or on VPC and have your own LLM endpoints available in your architecture, it’s possible to use Tabnine with the best LLMs available while keeping the entire solution entirely self-contained in your architecture, giving you the benefit of the best possible performance while also completely eliminating the risk of IP leakage of your company’s data and competitive advantage. Our internal testing and data have shown that Claude 3.5 Sonnet is the most performant LLM for software development tasks and — when combined with our agentic and RAG enhancements — significantly increases the speed at which engineers can complete every task in the SDLC and simultaneously boosts code quality, performance, maintainability, and security.
We’ve built a set of AI agents that work alongside your developers at every step of their development process. The benefit of these agents is that your developers don’t spend time writing 100-word prompts to get a meaningful response out of your AI code assistant. Our agents take the prompt engineering load off your engineers, enhancing and modifying the prompt entered by your engineers, layering on context from our RAG indexing, and sending the right query to the LLM with the right context, at the right time, for the task at hand.
In contrast with other AI code assistants or out-the-box LLMs, you’ll find that getting usable code from Tabnine is far easier due to our application layer of agentic and RAG enhancements that we feed into the query sent to the LLM.
The agents that generated the most excitement at AWS re:Invent were our Jira Implementation and Validation Agents, Testing Agent, and Code Review Agent.
Tabnine integrates with Jira with two button clicks. From there, each engineer can reference the Jira issues assigned to them by typing @Jira into the chat panel in their IDE or clicking the Jira button in the IDE chat. From here, executing Jira tickets is as simple as typing in “implement” and clicking two buttons. Tabnine reads the description and acceptance criteria from the Jira ticket, considers the local context from workspace indexing in the developer’s workspace, global codebase context from integrated repositories (like Github, Gitlab, or Bitbucket), and executes the Jira ticket.
And with our new Apply button, the workflow becomes even more seamless. Simply click Apply and Tabnine automatically inserts the generated code into the file exactly where it’s supposed to go. Of course, as with all our agents, the process is fully human in the loop with Tabnine explaining the changes it’s made, what the code does, and showing the diff in the code that your engineers can review inline or in the chat before accepting the change.
Tabnine is the only AI code assistant with a sophisticated testing agent, accessed through the beaker icon in your IDE chat. This agent automates the generation of comprehensive test plans considering the context of your code. If you have a test file already, you can point the agent at this file and it will read it and identify gaps in your test coverage as well as updates that need to be made to tests due to changes in your code. It returns a clear list of test cases with clearly understandable plain language descriptions.
From there, simply click a few buttons and Tabnine generates tests for each test case. These can also be modified with natural language prompting if desired, and then applied using Insert or the Apply button as desired.
Our Testing Agent has significantly reduced the engineering workload required to keep test coverage up to date and at your test coverage target when working in enterprise engineering teams with codebases that constantly change as new features are added and legacy code is updated.
Our customers have found that by using our precode review agents, the speed and volume at which they shipped code into review was significantly increasing. If code review wasn’t already a bottleneck at their organization, it certainly became one. That’s why we built and released our Code Review Agent.
You may have seen research from CISO organizations and cybersecurity vendors analyzing LLM-generated code and highlighting security issues with the code. The Code Review Agent solves all of that. We’re the only AI code assistant with a Code Review Agent that’s fully customizable to your organization’s unique coding standards and policies. The agent comes prebuilt with hundreds of code review rules that you can add to at any time.
We also train the agent on your organization’s unique code security, performance, and compliance standards. This can be achieved in two ways. First, if you have natural language documentation of your rules, we can feed that into Tabnine, enhance it and convert it into rule sets organized by language, category, library, and severity. If you don’t have rules documented, simply point Tabnine toward a golden repo with your best code and it can extract and develop a rule set for you.
Rules can also be configured by the user and team to your desire. This agent acts inside the pull request and reviews the code like a fully onboarded engineer at your company. It flags deviations, sets severity ratings for violations, and goes a step further to suggest modifications to the code to bring the pull request into full compliance with your standards. The agent is completely human in the loop: your code reviewer can review all suggested fixes in the pull request, ask for modifications, and then implement them directly in the pull request.
But there are more even agents. Learn more about our Code Fix Agent, Code Explain and Onboarding Agent, and Documentation Agent.
Our RAG models can intake context from more and more of your dev tools stack. We offer four levels of personalization that feed into our RAG model. The first level is local context awareness, which looks at 14 different data sources inside the IDE including variables, types, classes, chat history, cursor, highlights, @mentions, open files, dependencies, imported packages, and libraries, just to name a few. Just by turning on the first of four levels of personalization through our RAG model (local context awareness), our RAG produces a 40% increase in code acceptance rates.
That number climbs as you leverage our second level of personalization: codebase awareness (e.g., GitHub, Gitlab, Bitbucket) and noncode data source awareness (Jira/Confluence). The third (customized rule sets for your agents) and fourth level (model fine-tuning) offer the ultimate in customization.
These are all capabilities that we offer today. In plain English terms, unlike other AI code assistants, Tabnine actually produces code that fits your existing project, patterns, and company standards. We can do this because our RAG models are the most sophisticated models available on the market today.
Tabnine is the category leader and creator of the AI code assistant category. We’re willing to go head to head in any POC evaluation for enterprise engineering teams and we outperform all 12 of the major AI code assistant vendors in the space through our unique approach to maximizing AI performance and focus on delivering AI code recommendations that meet the unique engineering requirements relevant to your team, products, and codebase.
Tabnine supports over 600 languages libraries and frameworks; can be installed as a plugin for every major IDE; integrate with GitHub, Gitlab, and Bitbucket repos; can be deployed fully air-gapped or VPC; and are completely model agnostic.
If you’d like to get started evaluating Tabnine, simply contact us or chat with one of SDRs in our website chat. We’re well experienced in servicing the needs of large engineering teams at enterprise-level organizations. We can guide you through security and legal review, support you with an evaluation of Tabnine to get it into your engineers’ hands so they can experience the difference themselves, and have Customer Success and Solutions Engineering teams distributed across North America and Europe that can accommodate any time zone.
If you’d like an end-to-end demo of Tabnine, you can register for our weekly Office Hours sessions every Wednesday. If you’d like to take Tabnine for a spin yourself first, download our free plugin or sign up for a 30-day trial of our individual Tabnine Dev plan. These plans will not have the full set of agents, deployment, and RAG capabilities explained in this post, so if you’d like to try it all, doing an evaluation of Tannine Enterprise is the best way forward.
Thanks for joining us at AWS re:Invent!

State-of-the-art LLMs like Claude 3.5 Sonnet and GPT-4o have greatly improved the performance of generative AI applications, including AI code assistants. However, these LLMs are trained on vast amounts of data collected from all corners of the internet, including code that may have restrictions on how it can be used, introducing the risk of IP infringement. Since the copyright law for the use of AI-generated content is still unsettled, engineering teams at enterprises want to strike a balance: leveraging the performance gains that come from these powerful models while minimizing the likelihood of copyleft-licensed code getting in their codebase.
To support these goals, Tabnine is thrilled to announce Provenance and Attribution, a new feature that can drastically reduce the risk of IP infringement when using models like Anthropic’s Claude, OpenAI’s GPT-4o, and Cohere’s Command R+ for software development. Tabnine now checks the code generated within our AI chat against the publicly visible code on GitHub, flags any matches it finds, and references the source repository and its license type. This critical information makes it easier for you to review code suggestions and decide if they meet your specific requirements and policies.

It is well known that popular models like Anthropic’s Claude 3.5 Sonnet, Open AI’s GPT-4o, and Cohere’s Command R+ are trained on a large corpus of data. This includes publicly available information like content from websites, text on internet forums, and information in code repositories. Some of these repos contain permissively licensed code (for example, code with BSD, and MIT licenses) while many other repos contain code that has restrictions on how it can be used (for example, code with copyleft licensing like GPL).
A model’s training dataset is crucial in shaping its output, as LLMs inherently tend to replicate patterns from their training data. This means that third-party models like Claude 3.5 Sonnet and GPT-4o can potentially regenerate code that exists in their training dataset — including code with copyleft licensing. If you inadvertently accept such code suggestions, then it introduces nonpermissive code in your codebase, resulting in IP infringement.
In the past, Tabnine solved for this by offering a license-compliant model, Tabnine Protected 2, an LLM purpose-built for software development and trained exclusively on code that is permissively licensed. This model remains a critical offering, as many companies believe that even the use of an LLM trained on unlicensed software may introduce risk. With Tabnine’s new Provenance and Attribution capability, we’re more easily able to support legal and compliance teams that are comfortable using a wider variety of models as long as they specifically don’t inject unlicensed code.
Models trained on larger pools of data outside of permissively licensed open source code can offer superior performance (particularly in languages and frameworks where not much freely usable code exists), but run the risk of introducing nonpermissive code in their codebase. Tabnine’s Provenance and Attribution capability eliminates this tradeoff and offers the ability to choose between two levels of protection:
The Provenance and Attribution capability supports the full breadth of software development activities inside of Tabnine, including generating code, fixing code, generating test cases, implementing Jira issues, and more. After you invoke an AI agent or submit your prompt in AI chat, Tabnine checks the generated code against all the publicly visible code on GitHub.
If Tabnine finds a match, it notifies you within the chat interface and lists the source repo. Additionally, Tabnine informs you about the license type for the code in the repo (e.g., GPL, BSD, MIT). Since Tabnine reads code like a human, it not only flags the output that exactly matches the open source code, but also flags output if there are functional or implementation matches. This way, we flag cases where the overall function is the same, but the variable names are changed. Tabnine also keeps a log so that Tabnine administrators can keep track of the code that matches the open source code across the organization.
This feature makes it easy for you to review the output from Tabnine and determine if it complies with the requirements of your specific project, use case, or team.
In the near future, we plan to add a capability that allows you to also identify specific repos for Tabnine to check generated code against. For example, you can specify repos maintained by competitors, and thus ensure that your competitors’ code is not introduced in your codebase. In addition, we plan to add a censorship capability allowing Tabnine administrators to remove any matching code before it’s displayed to the developer. For example, the Tabnine administrator can censor any code with GPL licenses.
The Provenance and Attribution is currently in private preview and is available to any Tabnine Enterprise customer. Existing Tabnine Enterprise customers should contact our Support team to request access. Once enabled, the Provenance and Attribution capability works on all available models: Anthropic, OpenAI, Cohere, Llama, Mistral, and Tabnine.
Not yet a customer? If you’d like to learn more about how Tabnine can help you accelerate software development and ship better, more compliant code, we encourage you to reach out to us.
To learn more about the Provenance and Attribution capability, please check out the Docs or attend our Tabnine Live session on January 9 at 8 am PT.
AI is everywhere. Some form of AI-powered assistance is available for performing just about every life task you can think of: from planning vacations to designing a personalized workout regimen to composing a message for your mom’s birthday card. For these use cases, the chat interface to any generative AI model you utilize will typically return a reasonably decent result.
However, it turns out that many of us are also using AI to help us create, test, and deploy software — a situation where your choice of AI tools matters. A lot.
Why should you choose a dedicated AI code assistant like Tabnine over a large language model (LLM) like ChatGPT? Here are five important ways the two are different when it comes to writing (also debugging, updating, testing, and documenting) code.
Any interactive AI chatbot (like ChatGPT) rests atop one or more LLMs. LLMs are the core of AI: programs that use deep learning to analyze and understand huge amounts of data. LLMs are trained on vast datasets, typically millions of gigabytes of text from across the internet, to recognize, generate, and interpret human language.
Because LLMs are not specifically trained or optimized for coding tasks, getting good results requires a lot of context and additional information for writing code that will do a task properly. Developers must master the art of prompt engineering to coax forth the code they need. The user types in what they think is the right prompt query into ChatGPT, and then continues reprompting the LLM to eventually arrive at an accurate answer (unless they give up and just manually correct the code themselves).
Code assistants like Tabnine, however, enhance whatever the user asks inside of the chat interface by providing additional prompt information and context to generate a better outcome. The benefit is that the user can simply focus on the task and the “ask” and allow the AI code assistant to close the gap.
In addition, AI code assistants have built-in AI agents, which are a series of complex prompts and contexts that are stitched together to solve more specific problems, like a testing agent for creating unit tests or an onboarding agent that helps a developer that is new to a project get up to speed very quickly.
The core difference between LLMs like ChatGPT and dedicated AI code assistants can be summed up in one word: context.
When you ask ChatGPT for a code suggestion, the answer it returns is drawn from an LLM containing every imaginable kind of data available on the internet. What it’s not drawn from is your code. Because ChatGPT has zero awareness of anything outside the browser box, it can only return generic results. The AI has no context to understand whatever you’re working on. As a result, GPT requires you to include your own context and a lot of additional information in your prompts before it can return something even close to what you need.
LLMs are great at generating boilerplate code because no context is required. This type of code is so common that any model will have abundantly trained on endless examples. LLMs can also be good at generating small code improvements because you’re providing the context when you feed it the chunk of code you want it to work from.
What LLMs are not good at is giving anything better than generic, textbook-appropriate responses — versus an answer that matches your company or your team’s approach to solving problems. This happens because the LLM lacks the context to make suggestions that are specific to your code and your logic.
An example of this would be asking ChatGPT how to write a function to solve a specific problem. Without codebase awareness, it’s likely to give you a generic answer. With codebase awareness, though, an AI code assistant will reference the specific APIs or methods used within your company.
Tabnine, for example, can return personalized real-time results that are specific to your current work and right in your IDE because it has local context: awareness of the code available locally from your machine. This includes data from your IDE for information like variable types, comments you’ve added, open files you’ve interacted with, any imported packages and libraries, other open projects, and more. Tabnine also uses global context to return highly specific answers because, unlike ChatGPT, the tool can be connected with organization-level sources of information (like code repositories, design documents, Jira tickets, and more) to generate recommendations more aligned with a team’s way of working.
The other major advantage of an AI code assistant over an LLM is that you can ask questions about your codebase — and not just general coding questions. Instead of “how to” questions, you can ask “how do we” and “where do we” questions.
ChatGPT’s interface does make it very easy to ask for a function or code block, and you can then copy/paste whatever it returns into your IDE. The problem, though, is that ChatGPT’s answer is drawn from every imaginable kind of data available on the internet. Functions, funny limericks, food ideas for a birthday party — it’s all the same to ChatGPT because its underlying LLM, GPT, was designed for general-purpose processing tasks.
Tabnine, however, is designed specifically for programming tasks. Tabnine runs on its own proprietary models, one for code generation and one to power the code-oriented natural language chat agent. Tabnine’s LLMs are exclusively trained on code from credible open source repositories with permissive licensing. The baseline quality of the code it returns is substantially better because Tabnine’s AI was explicitly fine-tuned for code.
Public models simply cannot match the benefits of having models built around a discrete set of ultra–high-quality training data — including custom models trained on your specific codebases — the way a code assistant can. Furthermore, code assistants have deep and specific knowledge of languages and frameworks that are weak in public models due to the lack of public training data.
Also: Although ChatGPT is limited to a single LLM (it can only ever query GPT models), Tabnine lets users choose to add additional LLMs for the code assistant to draw from (including, actually, GPT, plus Claude, Mistral, Cohere, and others).
Probably the biggest advantage of working with ChatGPT is how easy it is to plug prompts into its browser interface. It gets more complicated after that, though, as you need to keep copying and pasting snippets back and forth between the site and your IDE. (There are ways to incorporate ChatGPT into your IDE, although these are cumbersome and highly manual to implement while also being nowhere near as powerful as running a code-specific AI assistant).
Tabnine, on the other hand, works locally and inside your IDE, where it can act on your code directly. Because it has this tight integration with your IDE, Tabnine’s generative inline code suggestions, autocompletions, and responses to prompts as comments are real time and, more importantly, highly accurate and context appropriate.
Tabnine also has an AI chat agent that integrates into your IDE along with its generative and code completion functions. You can type into a chat box using natural language and ask the agent to, for example, explain some code, have a back-and-forth conversation to work through some logic, or help refine a more comprehensive prompt — any topic or issue you would search for on Stack Overflow or even chat about with a coworker.
Tabnine is far less disruptive to workflow because you never have to pop out of your IDE to a browser to query ChatGPT or any other source — everything you need is right there.
When you use ChatGPT, OpenAI collects data from your interactions with ChatGPT and uses your data to continue training their LLMs:
We retain certain data from your interactions with us, but we take steps to reduce the amount of personal information in our training datasets before they are used to improve and train our models. This data helps us better understand user needs and preferences, allowing our model to become more efficient over time.
ChatGPT saves everything — not only your prompts and the AI’s responses, but also geolocation data, network activity, and what device you’re using. Oh yeah, and your email address and phone number. According to Open AI’s privacy policy, this data is used to train the LLM and improve its responses, but the terms also allow the sharing of your personal information with affiliates, vendors, service providers, and law enforcement.
It’s not just ChatGPT — many (if not most) generative AI tools, LLMs, and chat assistants alike, retain your data for their model to train on. Buried deep within their terms of use is language specifying that they can use your code, data, and behaviors to feed their platform’s models, making your information available to anyone (and everyone) using that platform.
Even if any code you share with ChatGPT (to provide it with context, as above) does not contain sensitive information, it can still contain some knowledge that you may not want to share with others. Many developers follow the guideline, “If you’d not be comfortable posting something on Stack Overflow, don’t paste it into an unsecured LLM.” Unfortunately, that advice also applies to some AI code assistants currently in the market. It’s also worth noting that sharing code with any LLM may be a violation of your corporate policies or your employment agreements (or contracts, if doing work for others).
ChatGPT does offer the ability to opt out of their default opt-in data sharing and retention settings, but doing this comes at a cost. Limiting the LLM’s data collection reduces ChatGPT’s functionality because it will not “remember” anything from your previous chats — so the code suggestions it returns will devoid of context. Any results will now come from a limited set of generic algorithms, resulting in even less accuracy and relevance than the already limited code personalization ChatGPT offers when you completely share all your data.
Tabnine, on the other hand, is built by people who understand all the reasons why developers aren’t comfortable sharing their data externally. Tabnine’s code assistant never retains any code: requests are only ephemerally processed to provide coding suggestions, and then immediately discarded. Any data transmitted between the user’s machine and Tabnine servers is encrypted, securing against eavesdropping or attacks.
Finally, LLMs (and some other code assistance tools) use third-party APIs or models to deliver their services. Tabnine, however, uses proprietary models (constructed with knowledge gained over more than a decade of working in generative AI) so there’s no risk of your code being shared.
Another privacy and security feature not available from LLMs is the ability to control deployment location. If your company policy prefers or requires private deployments, Tabnine can be deployed on-premises for you to maximize control; deployed as single-tenant SaaS for convenience; or deployed on a VPC as a balance of the two. If it’s truly critical for your data to never leave your perimeter, ever, the assistant also supports fully air-gapped deployments where there’s no network path outside your environment.
For software engineers, choosing a dedicated AI code assistant like Tabnine over a general-purpose LLM such as ChatGPT is the difference between writing code in a text editor and pushing it to a live prod environment, versus using an IDE and a VCS. Both allow you to get the job completed, but only one approach is tailored to how you work. AI code assistants like Tabnine are enterprise-grade tools designed exclusively for software development tasks, while ChatGPT is a general-purpose chat bot designed to answer a broad variety of questions. Because Tabnine leverages fine-tuned models and can tap into the deep context of your code and requirements, the AI is able to return higher quality and more relevant code suggestions.
While ChatGPT can provide code snippets based on broad knowledge, the LLM doesn’t know anything about your code. ChatGPT operates without awareness of the specific project or codebase a developer is working on, leading to more generic suggestions that require significant user input and can require major correcting.
Tabnine specifically uses sophisticated and nuanced context based on both local and global awareness of your code and company standards to return highly personalized code recommendations that are the opposite of generic. And Tabnine’s tight integration also ensures a smoother workflow, since developers can receive real-time assistance with their coding questions without leaving their coding environment.
Privacy also differs radically between the two. Coding with an LLM like ChatGPT requires feeding in your own, potentially proprietary, code for it to work from — prompts and associated code it can then retain and use for training its models. Tabnine, on the other hand, puts you in total control. Your code is never stored, never used as training data, and never shared with external applications or services.
Specialization. Personalization. Integration. Privacy. These are the five pillars of Tabnine’s AI coding assistant — and they’re also five things that ChatGPT and all other LLMs simply do not, and cannot, give to developers.
In today’s fast-paced software development environment, AI code assistants have transitioned from niche tools used by individual developers to essential resources for entire engineering teams. Among these, Tabnine stands out by offering a highly personalized AI experience tailored to the specific needs of each organization. This article explores how Tabnine goes beyond universal models to deliver precise, context-aware coding assistance, thereby enhancing developer productivity and efficiency.
AI code assistants, powered by large language models (LLMs), have shown significant potential in boosting developer productivity. However, their universal nature often results in generic recommendations that lack the specific knowledge of an organization’s codebase, architecture, and coding practices. This is where Tabnine excels. Our personalization engine enables Tabnine’s AI agents to intake, prioritize, and understand every developer, team, and organization’s context.
Tabnine enhances its AI capabilities through four levels of progressive personalization, ensuring that its recommendations are highly relevant and tailored to the organization’s needs. These levels include:
Tabnine employs advanced retrieval methods to deliver precise and tailored suggestions:
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG): This method enhances LLM performance by integrating relevant documents from an organization’s codebase into the model’s prompt, thereby improving the accuracy of generated responses. The process involves chunking code into manageable pieces, embedding these chunks, and querying a vector database to retrieve relevant documents. This approach ensures that the AI’s responses are informed by the most relevant and current information available.
Semantic memory RAG (SEM-RAG): SEM-RAG goes a step further by using static analysis to understand the semantic relationships within a codebase. This allows Tabnine to retrieve contextually relevant code elements even from imported libraries, enhancing the model’s ability to provide precise recommendations based on user-specific information. This method ensures that even complex and interconnected codebases are well-understood by the AI.
Tabnine has developed a set of AI agents that you can access through chat, quick commands, and Code Lens buttons from inside your IDE. Using our prebuilt AI agents lets developers quickly execute every step of the software development life cycle. Unlike generic AI code assistants, Tabnine’s AI agents do the heavy lifting of prompt engineering for you. Below we’ve detailed two example use cases documentation and testing that help you understand what our AI agents take care of for you.
For example, if you were to use a nonagentic AI code assistant to assist with code documentation, you might need to write a prompt with the following degree of detail to get a response that you could immediately implement:
“I am providing you with a Java code file that includes classes for generating passwords, checking password strength, and providing useful password guidelines. Here is what I need you to do with the code:
Carefully read through each function and class in the code. Add comprehensive inline documentation for every function, method, and class. Use JavaDoc-style comments, so the documentation is structured and standardized. Each class should have a high-level comment explaining its purpose, any dependencies, and its interactions with other classes.
Each method should include: A description of its purpose. Explanations of all parameters (if any) and their expected values. A description of the return value, if applicable. Any potential exceptions the method might throw and under what circumstances. For any loops, conditionals, or key operations, provide brief comments explaining what is happening and why it is necessary. Ensure the documentation provides clarity for future developers who may work on or maintain this code. Provide the fully documented code with inline JavaDoc comments.”
With Tabnine, you could achieve the same result in seconds. All the input that would be required from a user would be two button clicks: one to activate workspace indexing and a second to use the Documentation Agent with a concise chat prompt “please document the code in @calculator.java”
Through our codebase connection feature, Tabnine would automatically recognize that the documentation in the Java code in your codebase is written in inline JavaDoc format. The local IDE context awareness would intake the file and all contextually relevant elements creating documentation that seamlessly fits into your IDE and codebase.
As another example, were you to use a nonagentic AI code assistant for generating tests, you’d need to write a prompt like:
“Create a new Java test file in a structure that aligns with the Java testing framework, preferably JUnit 5. Write unit tests that cover each function individually to ensure that every line and branch of code is tested.
For the Password class: Test the constructor to ensure it initializes the values correctly. Test the CharType method to confirm it accurately classifies characters as uppercase, lowercase, digits, or symbols. Test PasswordStrength and calculateScore to confirm they return the correct password strength rating based on a variety of password inputs (weak, medium, strong).
For the Generator class: Test the GeneratePassword function with different length inputs and various inclusion settings for uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols to confirm it generates the correct password formats. Ensure mainLoop and other user-interaction methods function as expected by simulating inputs. Include edge cases, such as zero-length passwords or requests with no character types selected. Ensure the unit tests have full coverage for every function, and validate that the expected output or exceptions match the actual results.
Provide a separate file containing the JUnit test cases, along with a brief summary of how to execute these tests and verify code coverage.”
With Tabnine, you could simply click on the beaker icon to have Tabnine @ reference all relevant files and code repositories if prioritizing context is desired. Tabnine would then generate a comprehensive testing plan with explanations for each test case. You could then review the tests suggested and ask Tabnine to further refine each one if desired. Tabnine would also automatically generate a new testing file or if you already have an existing testing file, Tabnine would read that file to identify gaps and optimizations further guiding the test generation.
This becomes particularly important when you’re working on maintenance tasks, as being able to feed and direct testing context into your AI can save you hours of time when you need to adjust your testing to accommodate changes that have been pushed into your codebase from when the tests were first built.
These are just a few examples of the many ways Tabnine personalizes our AI agents to your relevant context. We’ve also created a whole suite of additional AI agents:
As you’re moving through each step of your SDLC — plan, create, test, fix, document, explain, maintain — Tabnine’s personalized AI agents make working with an AI code assistant fit seamlessly into your workflow. After all, you’re an engineer, not a prompt engineer. Tabnine fits seamlessly into your workflow because the AI code assistant you use should adapt to you — you shouldn’t have to adapt to your AI.
Tabnine is the AI code assistant that you control. That means every aspect of the AI is personalized to your organization. We’ve already covered how that works with our AI agents and the first three levels of personalization.
What you may not be aware of is that you also have the option to switch the underlying LLM powering the AI agents. Our personalization and agentic enhancements are fully model-agnostic. You use our model switcher dropdown in your IDE to switch between eight different first-party and third-party LLMs in real time.
The AI space is the fastest moving and progressing technology sector in human history and Tabnine is designed with model flexibility in mind. You can choose from the latest models from Anthropic, Cohere, OpenAI, IBM, Mistral, Tabnine, and others — all LLMs are included in your Tabnine Plan.
Furthermore, if you’re a Tabnine Enterprise customer, we give you additional optionality. Got your own API endpoint for an LLM? You can connect that into Tabnine and offer it inside the IDE plugin to your organization and leverage the agentic and personalization enhancements we’ve made. Developed your own model? No problem, you can connect that, too.
The capabilities of LLMs continue to grow and evolve, but as you may have noticed recently, OpenAI delayed the launch of their new Orion model. The publicly available training data that LLM providers can access is discrete and limited, and the majority of this data has already been consumed and trained on. Further improvements in LLM performance for software development tasks can only be achieved through improving personalization engines. Can the LLMs you use intake your organizational data and leverage that context effectively to improve the code response? That’s what Tabnine excels at. Furthermore, unlike other AI providers, the context we intake is never stored, never used to train our universal models, and isn’t shared with third parties.
We believe that only your organization should benefit from your IP and using Tabnine gives you the advantage of maximizing AI performance while eliminating the risk of exposing sensitive data to third parties who would then consume and train their LLM on the data, essentially giving your competitors parity and access to your company’s innovations, destroying your advantage in the market.
As this continues to evolve, we’re seeing an uptick in the desire for mature, sophisticated engineering organizations to run their AI entirely on-premises, and in some cases, fully air-gapped. Tabnine was the first to support fully private deployments. But an interesting roadblock you may run into is that large LLMs need large amounts of compute power, creating a challenge in costs and acquiring adequate GPUS to utilize the LLM.
As we predicted months ago, the market is starting to shift towards highly specialized small language models. For example, IBM launched a model that excels at Cobol. It’s likely that your organization will develop such models or adopt them over time, as well as deploy them on-premises. With Tabnine, you’re future-proofing your AI code assistant provider: as you adopt SLMs and LLMs and deploy them on-premises, you’ll be able to connect them to Tabnine and layer on our deep integrations with your tech stack, AI agents, and personalization engine to maximize their impact.
What if your codebase is primarily composed of languages that are poorly supported in open source or widely available training data? For example, System Verilog, VHL, or VHDL to name a few. Or what if your organization uses its own markup language or has very complex, highly specialized, large repositories? That’s when model fine-tuning, Tabnine’s fourth level of personalization, is useful.
When retrieval methods are insufficient, especially for highly specialized or extensive codebases, Tabnine offers fine-tuning capabilities for code completions. Fine-tuning involves adjusting the model to better align with an organization’s unique code and practices. Tabnine utilizes parameter-efficient tuning techniques, such as low-rank adaptation (LoRA), to perform fine-tuning effectively. This method adds new weights to the model without altering the original ones, maintaining the model’s overall integrity while enhancing its performance on specific tasks. This allows organizations to create highly specialized AI models that perfectly fit their unique requirements.
Tabnine supports the deployment of multiple fine-tuned code completion models within the same server, allowing organizations to route completion requests based on programming language or user identity. This flexibility ensures that each department or project can benefit from a model tailored to its specific needs, optimizing overall productivity. By allowing different models to coexist and be used selectively, Tabnine ensures that the right tool is always available for the job.
Tabnine’s approach to personalization sets a new standard in AI-driven software development. By integrating context-aware, connection-driven, and customizable features, Tabnine elevates the capabilities of traditional LLMs, making them highly relevant and effective for organizational use. This personalized approach not only enhances developer productivity but also ensures that AI-generated code aligns with the specific requirements and standards of the organization.
In a rapidly evolving tech landscape, it’s critical to have the ability to tailor AI tools to fit the unique needs of an organization. Tabnine’s commitment to personalization transforms AI code assistants from generic tools into indispensable assets for modern engineering teams, paving the way for more efficient, accurate, and tailored software development processes.
Finding and fixing bugs and errors in a large, enterprise-grade application can be like finding a needle in a haystack. And once you do find the issue, figuring out a suitable fix can be equally difficult, sometimes causing other issues to sprout up that require additional changes. No developer enjoys spending their time being a bounty hunter for errors and issues, yet every developer spends a significant amount of time every week doing remediation work.
Tabnine’s Code Fix Agent empowers developers to fix errors and bugs within their code with the click of a button or a simple command (/fix-code). It ingests any error messages coming from the IDE (if there are any), the code and data in your IDE, and information in your global codebase as context to suggest personalized, accurate improvements to your applications that meet your development organization’s intent.
Tabnine’s Code Fix Agent is seamlessly integrated into Tabnine’s user experience in two different form factors.
Within the Tabnine AI Chat, users can invoke the agent by clicking the Fix code button when starting a new conversation or by typing /fix-code within the prompt bar. The Tabnine Code Fix Agent prompts you to select a block of code within your file and then provides personalized suggestions to fix the errors or bugs within the selected code. You can then hit Insert to add Tabnine’s suggestions to your code file.
If you’re already in your coding flow, you can access the Code Fix Agent within the Inline Actions form factor, either by using the Command Palette (accessible by using the ⌘ + I hotkeys on a Mac) to navigate to the Quick commands dropdown, or by typing /fix-code within the prompt bar. You can also use Codelens at the top of each block of code to generate a personalized suggestion to solve the issues within your code. The Code Fix Agent returns suggestions to fix the selected code in your file shown through a simple diff view, allowing you to clearly see the suggested changes that you can accept, reject, or refine.
For generative AI to truly be impactful, context is everything. Without it, large language models (LLMs) tend to produce responses that, while accurate, are often generic and less aligned with your engineering team’s unique practices. With the right context, however, an AI code assistant can tailor recommendations to fit your team’s specific coding patterns, improving reuse and alignment.
Tabnine achieves this by using locally available code and data within your IDE as context. This includes variable types near the completion point, comments you’ve written, files you’ve interacted with, imported libraries, active projects, and more. By tapping into these sources, Tabnine delivers more relevant and personalized suggestions. Tabnine Enterprise administrators can connect Tabnine to their organization’s code repositories, further expanding the contextual information available. This drastically enhances Tabnine’s ability to suggest accurate fixes and code suggestions that align with your team’s workflow and standards.
The benefits the Tabnine Code Fix Agent provides are vital to a development organization of any size. Developers will spend less time working through bug and error issues, allowing them to do what they do best: innovate. And organizations will ultimately move faster, developing more innovative products much faster due to engineering resources being more effectively used.
The Code Fix Agent is available for all Chat users and is compatible with all IDEs that support Tabnine Chat. Check out our Docs to learn more.
In addition to the Code Fix Agent, Tabnine offers numerous AI agents to accelerate your software development life cycle, including the Code Review Agent, Jira Implementation and Validation Agents, Testing Agent, Code Explain and Onboarding Agent, and Documentation Agent.
If you’re not yet a customer, you can sign up for a free trial of Tabnine. Want to learn about all the plans Tabnine offers? Visit our Plans & Pricing page.
Producing high-quality, secure code is just as important as ensuring it’s well documented. Documentation makes it easier to understand the purpose and functionality of the code. It increases the readability and makes it simpler to maintain and update the code in the future.
However, creating documentation is not at the top of the wishlist for most developers, who’d rather spend their time building new features. As a result, it’s common to have documentation that’s incomplete, difficult to follow, or outdated as the codebase evolves.
Tabnine’s Documentation Agent enables you to generate documentation that meets your organization’s standards faster and easier than ever. With one click, you can create comprehensive documentation (including formal documentation of classes and functions for API guides and comments) for your code. The agent allows you to offload the mundane task of creating docs to Tabnine so you can focus on building features that add value to your customers.
The Documentation Agent is fully embedded into Tabnine, gaining context from your local IDE and connected codebases and instantly creating personalized documentation. Let’s cover the several ways in which you can use it.
Within Tabnine AI Chat, users can invoke the agent by selecting the Write docstrings for code button when starting a new conversation or by typing /document-code within the prompt bar. The Documentation Agent will prompt you to select a block of code within your file and the chat will return documentation for that selected code. You can then hit Insert to add Tabnine’s suggestions to your code file.
Nested within the Inline Actions form factor, use either the Command Palette (accessible by using the ⌘ + I hotkeys on a Mac) to navigate to the Quick commands dropdown or by typing /document-code within the prompt bar, or use Codelens at the top of each block of code to generate documentation. The Documentation Agent will return suggested documentation for the selected code in your file, which the user can accept, reject, or refine.
In generative AI, context is everything. Without context, LLMs will typically generate responses that are textbook accurate but generic, and thus less aligned to what your engineering team finds acceptable. With context, an AI code assistant will make recommendations that consider your team’s patterns and will more often do better with reuse.
To achieve this, Tabnine leverages locally available code and data in your IDE as context to offer more tailored responses, including variable types used near the completion point in the code, comments you’ve added, open files you’ve interacted with, imported packages and libraries, open projects, and many more sources.
Additionally, Tabnine Enterprise administrators can also connect Tabnine to their organization’s code repositories, significantly increasing the context that Tabnine uses to provide responses to documentation.
Developers can generate documentation that’s not only personalized to their organization’s standards and best practices, but they can do it much faster than ever before. For organizations, the Documentation Agent provides development organizations with scalable, fast documentation generation that follows best practices and coding standards at an organizational level, allowing your developers to focus on what’s most important, launching new features.
The Documentation Agent is available for all Tabnine Chat users and is compatible with all IDEs that support Tabnine Chat. Check out our Docs to learn more.
In addition to the Documentation Agent, Tabnine offers numerous AI agents to accelerate your software development life cycle, including the Code Review Agent, Jira Implementation and Validation Agents, Testing Agent, Code Explain and Onboarding Agent, and Code Fix Agent.
If you’re not yet a customer, you can sign up for a free trial.
We’re offering an exclusive, limited-time deal for developers this Cyber Monday: 50% off Tabnine! You can upgrade your development tools at an amazing price with this once-a-year opportunity.
Why should you upgrade to Tabnine Dev? Because you’ll enjoy all the benefits of AI-driven development with the best personalized AI code assistant:
AI software development assistance via chat
Streamline your workflow with instant AI support directly through chat for all your coding needs.
Powerful AI agents
Use AI agents to generate and explain code, create tests, fix bugs, write documentation, and even implement and validate Jira issues, saving you countless hours.
Personalized AI recommendations
Benefit from AI suggestions that are fine-tuned to your existing code standards, helping you maintain consistency and improve code quality.
Seamless LLM switching
Easily switch between large language models (LLMs) to suit your specific project needs, ensuring you have the best support for every task. Choose from popular third-party LLMs like Claude 3.5 Sonnet, GPT-4o, Command R+, Codestral, and Tabnine’s proprietary models.
Access to advanced LLMs, without usage limits
Enjoy unlimited usage of advanced LLMs, giving you unparalleled flexibility and power without worrying about usage caps.
Protection
Count on enterprise-grade security, safety, and privacy, and get access to models exclusively trained on permissively licensed code.
Support
Ticket-based support is available during business hours.
Don’t miss out — this limited-time offer ends Sunday, December 8! Now’s the perfect time to take your coding to the next level with a massive discount and boost your productivity and efficiency with Tabnine’s powerful AI tools.